An External Benefit From a Transaction Is a Benefit to:
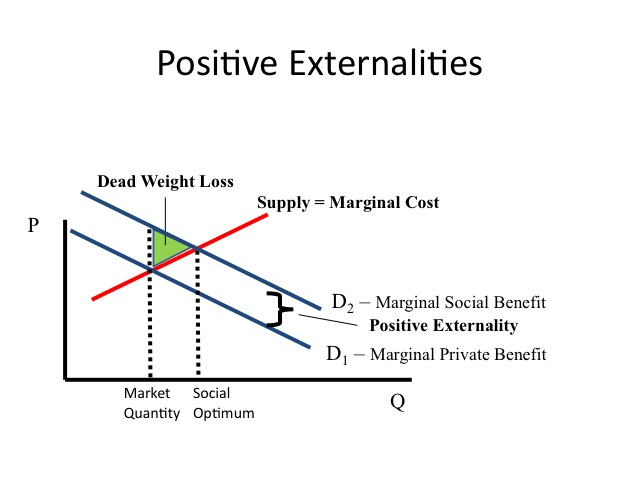
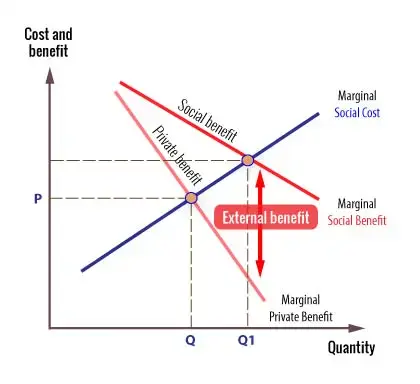
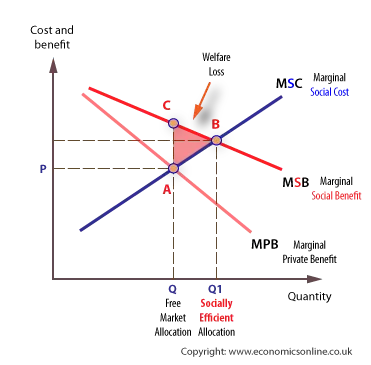
For example if the marginal social benefit at A is 5m and the marginal social cost at C is 10m then the net welfare loss of this output is 10m 5m 5m. External benefit positive externality.
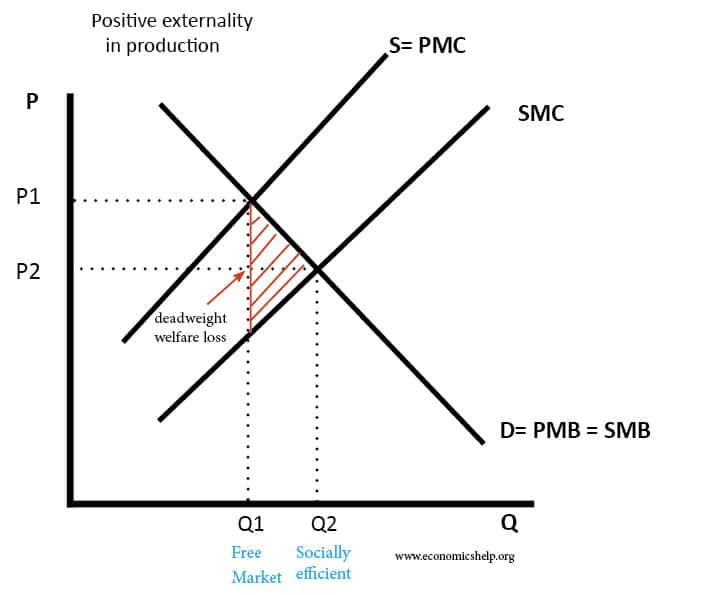
Externalities Definition Economics Help
App Store Google Play.
. View and print your eStatements. X12 defines and maintains transaction sets that establish the data content exchanged for specific business purposes and in some cases implementation guides that describe the use of one or more transaction sets related to a single business purpose or use case. Get Personal Financial Management PFM in a single login.
Bank anywhere 247 with our mobile banking app. External effect A positive or negative effect of a production consumption or other economic decision on another person or people that is not specified as a benefit or liability in a contract. Air pollution from motor vehicles is one example.
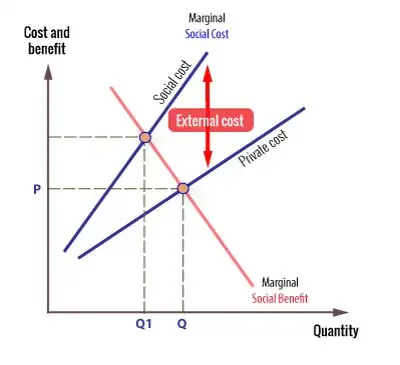
However if we add external costs the socially efficient output is Q1 at point B. Costbenefit analysis CBA sometimes also called benefitcost analysis is a systematic approach to estimating the strengths and weaknesses of alternativesIt is used to determine options which provide the best approach to achieving benefits while preserving savings in for example transactions activities and functional business requirements. At Q marginal social costs at C are greater than marginal social benefits at A so there is a net loss.
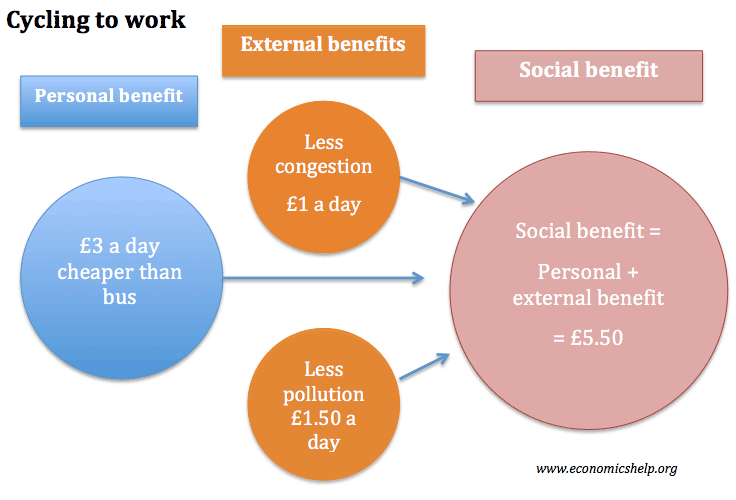
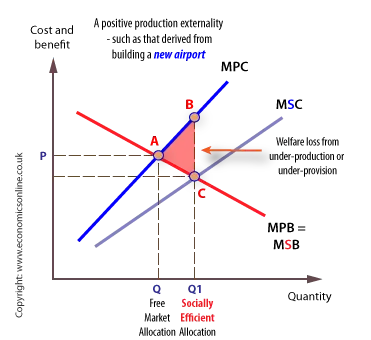
Costs inflicted on others such as pollution and congestion that are worse because you drive to work are termed external diseconomies or negative externalities while uncompensated benefits conferred on others are external economies or positive externalities. The diagrams on the following pages depict various exchanges between trading partners. The cost of air pollution to society is not paid by.
External benefit positive externality. Pay bills and view your payment histories. Benefit from added fraud prevention and security features.
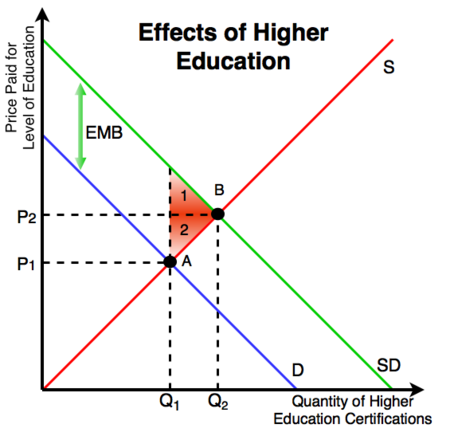
In economics an externality or external cost is an indirect cost or benefit to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another partys or parties activity. Externalities can be considered as unpriced goods involved in either consumer or producer market transactions. It is called an external effect because the effect in question is outside the contract.
What can be easier than having your own mini-branch in your pocket.

5 1 Externalities Principles Of Microeconomics

Explanation Of The Reasons For And Consequences Of Market Failures Reflect On Cost Benefit Analysis The Causes Of Market Failures Consequences Of Market Ppt Download

Externalities Edexcel Economics Revision
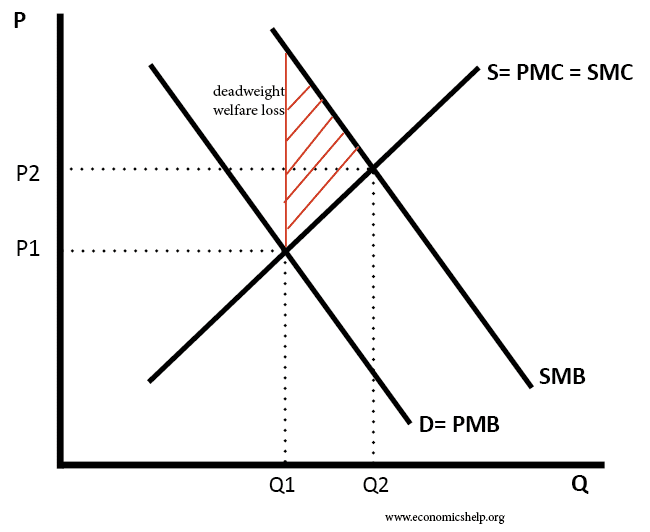
Positive Externalities Economics Help
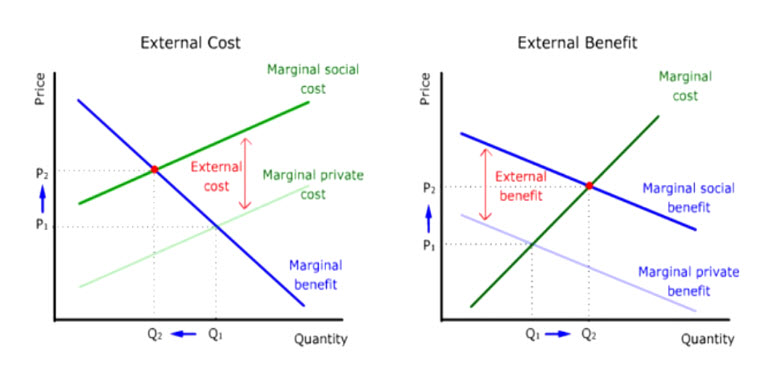
Living Economics External Benefit And External Cost Transcript

Market Failure Unit 1 Market Failure Unit 1 Aim To Understand Externalities Objectives Define Market Failure And Externalities Describe Positive And Ppt Download
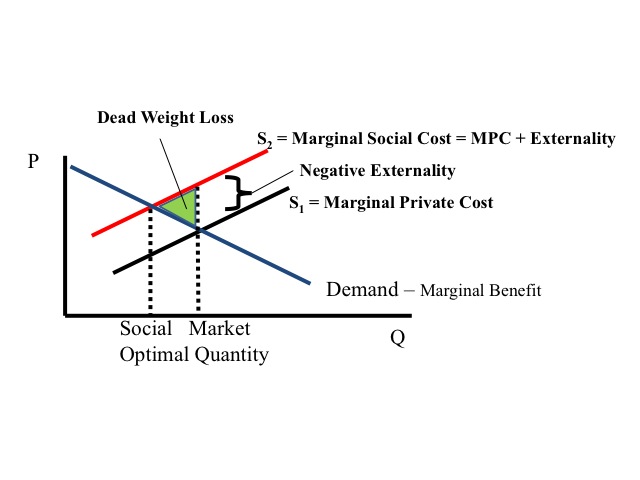

Comments
Post a Comment